AR vs VR : Understanding the Core Differences
The development of Educational Technology has transformed how students engage with learning resources. Among the most innovative breakthroughs in this sector are Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Although these technologies produce immersive learning environments, they vary in their operation, user interaction, and learning impact. This article explores the main differences between AR and VR in EdTech, as well as their advantages, disadvantages, and potential future applications in education.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality enhances the real world by seamlessly integrating digital elements like images, sounds, and 3D models. Unlike Virtual Reality, which immerses users in a completely virtual space, AR overlays virtual content onto the physical environment without replacing it. This technology is widely accessible through smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, making it easy to use in everyday settings.

How AR Works
AR uses a mix of hardware and software, such as cameras, sensors, and computer vision, to identify things in the real world and superimpose digital data on top of them. This data can be presented in a number of ways, including text, audio, animations, and pictures. In order to improve user experiences, augmented reality (AR) applications frequently make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time data processing.
AR in Edtech
By making traditional learning more dynamic and interesting, augmented reality, or AR, is having a significant impact on the EdTech industry. Students can investigate topics like the solar system, human anatomy, or historical landmarks in 3D with the use of augmented reality (AR)-based applications, which simplify difficult subjects. It gives studying a more practical component, which keeps students engaged and improves their memory of the material. Additionally, coding platforms and STEM instruction kits are utilizing AR to let students see their work come to life in authentic environments. Virtual field trips are made possible by programs like Google Expeditions, which bring distant locations into the classroom. Teachers can also profit from AR by using it to simulate classroom situations and provide realistic training.
What is Virtual Reality?
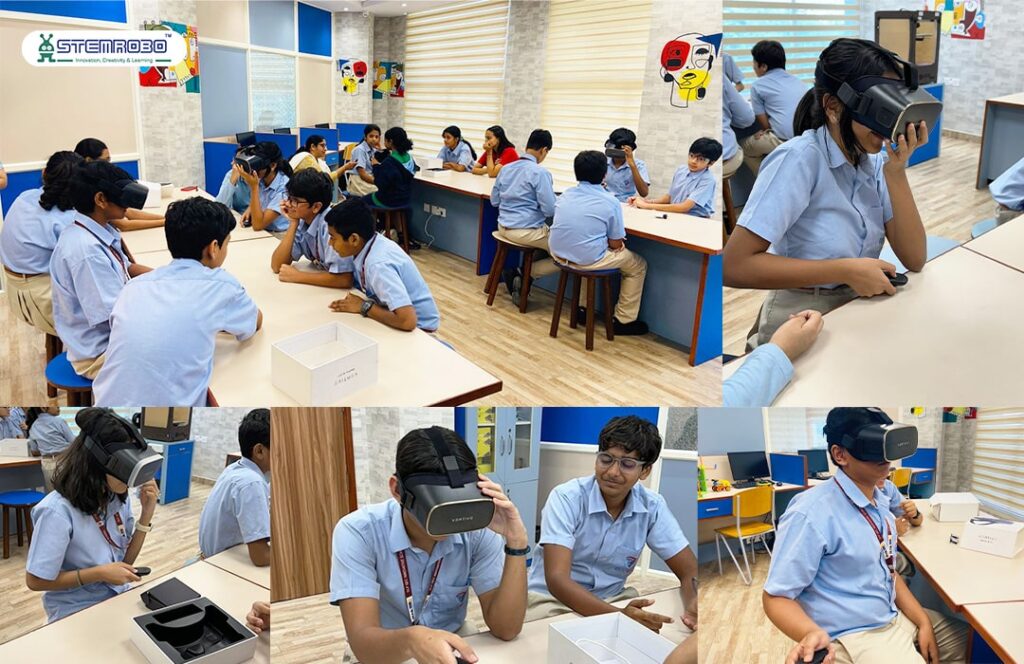
By isolating users from the outside world and allowing them to interact with realistic objects, spaces, and scenarios, virtual reality (VR) creates an immersive digital environment that allows users to fully immerse themselves in a simulated world. VR is particularly useful for simulations, skill-based training, and interactive lessons, which help students understand complex concepts through hands-on experience rather than just theory. VR improves engagement and gives a deeper understanding of subjects in a way that traditional methods cannot give generally.
How VR Works
As it provides completely immersive, hands-on experiences, virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing the way students learn. Through the use of controllers, motion sensors, and headsets, virtual reality (VR) produces a 360-degree virtual world in which students can walk around and engage with their surroundings. Students may experience teachings in a far more engaging way, whether they are completing a science experiment, seeing a historical landmark, or investigating the human body. Virtual reality (VR) makes learning seem thrilling and real by stimulating sight, sound, and occasionally even touch. It’s a fantastic method to keep children engaged in their study and simplify difficult subjects.
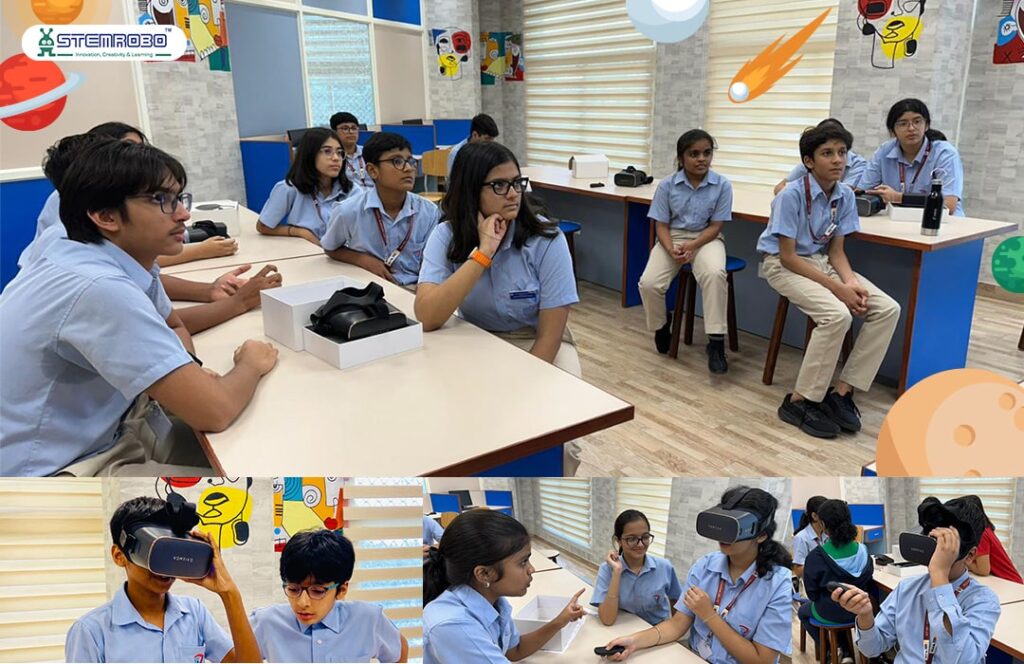
VR in Edtech
In the EdTech space, virtual reality (VR) is growing in strength and providing students with more interactive and interesting learning opportunities. It’s particularly helpful for training—engineering students can learn how complicated machinery operate, pilots can experience flight simulations, and medical students may safely perform surgeries—all without the risks of the real world. Through virtual field trips that allow students to see well-known locations, museums, or natural sites from anywhere, virtual reality (VR) also brings the outside world into the classroom. It aids in the demonstration of psychological treatments such as exposure therapy for PTSD or phobias. Through virtual classrooms where teachers and students can interact as avatars, virtual reality (VR) even strengthens the sense of connection in remote learning. It’s a fantastic method to increase the effectiveness and immersion of instruction.

Core Differences between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality With their own distinct advantages, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are revolutionizing education. AR is frequently utilized in interactive textbooks and digital learning tools, providing students to explore 3D models and animations superimposed on the real world using a phone or tablet; it improves classroom experiences by providing additional information during field trips it aids in visualizing scientific experiments; and it makes literature come to life through augmented storytelling, in medical studies, AR supports learning by allowing students to examine anatomical structures in a more visual and interactive manner for language learners, AR can instantly translate words in real contexts, making it easier to naturally understand new languages, and it is useful in blended learning. Virtual reality main characteristics represented in imaginary space, immersion in virtual space, sensory feedback and interactivity while augmented reality includes contextuality, which means combination of virtual and actual world simultaneously, interactivity at the same time and spatiality in the 3D world.
While Augmented Reality (AR) enhances learning by imposing digital elements into physical surroundings, Virtual Reality (VR) on the other hand offers a fully immersive experience, making it an excellent choice for self and, in-depth learning that requires complete focus and engagement. VR transports students out of their physical surroundings and places them into a completely digital environment, making it ideal for virtual classrooms, lab experiments, and training. In contrast to simply viewing content on a screen, VR immerses students in a 3D world where they can interact with objects just as they would in real life. This makes VR especially useful for virtual field trips, allowing students to explore historical landmarks, remote locations, or even fictional worlds that would otherwise be impossible to visit.
Which One is Better?
The question is not which one is better, but rather which one is more suitable for a specific purpose. Augmented Reality enhances real-world experiences, while Virtual Reality is ideally used for fully immersive experiences. For example, students might use AR to explore the human body through AR-enabled textbooks. On the other hand, VR offers fully immersive environments that allow students to work in a virtual lab without physical limitations or risks. In every field both AR and VR offers unique benefits tailored to different learning needs.
Conclusion
In our quest for more immersive digital experiences, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) offer two different but complimentary avenues. While VR provides total immersion into virtual worlds, AR adds digital overlays to the real world. Both technologies have amazing promise in a variety of fields, including business, entertainment, healthcare, and education. We can better appreciate each of their unique capabilities and see how they can influence our digital future when we are aware of their fundamental differences. Regardless of whether you like AR’s improved realism or VR’s complete immersion, one thing is certain: these technologies constitute the cornerstone of a new era of interaction.